hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides|Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides : Clark Glucose formation rate r1 and r2 over AC-SO 3 H and Amberlyst 70 catalysts, respectively, and the catalytic activity ratios of r1 / r2 for the hydrolysis of various disaccharides and malto-oligosaccharides. .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
PH0 · Polysaccharides
PH1 · Monosaccharide composition analysis of polysaccharides from natural
PH2 · Monosaccharide composition analysis of
PH3 · Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides on
PH4 · Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides
PH5 · Hydrolysis of Carbohydrates Chemistry Tutorial
PH6 · Hydrolysis of Carbohydrates
PH7 · Hydrolysis (video)
PH8 · Experiment
PH9 · Carbohydrates (article)
PH10 · 1.4 Condensation & Hydrolysis
Spankbang Con Porn Videos! - Www Spankbang, Spank Ang, Spankbang Porn - SpankBang. en ; Login Sign up Sign up for FREE ; Videos . Trending Upcoming New Popular. HD 12m. 2.2K 100% 20 hours. NURU MASSAGE - Gorgeous Busty Masseuse Jasmine Jae Is Horny To Suck An.. HD 15m. 26K 95% 1 day.Bet on Football with William Hill's online Football Live Streaming Matches coupon. Great odds and great excitement from the world's top online bookmaker. . Cash In My Bet - bets placed on this market can be cashed in in-play (as long as betting is still available on the market). For information on how to Cash In your bet click here. 13 Sep:
hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides*******Polysaccharides can be hydrolysed under acidic conditions. Acid hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides produces monosaccharides by breaking the glycosidic links (ether bonds) between monomer units in the structure of the molecule. Hydrolysis is a process in which water is added back into a molecule to break it apart. This is the process by which digestion occurs. After we consume a carbohydrate,. When Seliwanoff’s reagent is reacted with a disaccharide or a polysaccharide, the acid in the solution will first hydrolyze them into monosaccharides, .
Polysaccharides are insoluble so have less influence on the process of osmosis. Disaccharides and polysaccharides are formed when two hydroxyl (OH) groups on . Conventionally, mineral acids 5, 6 and enzymes 7 are used for the hydrolysis of polysaccharides. However, mineral acids entail difficulties of product separation, the .Glucose formation rate r1 and r2 over AC-SO 3 H and Amberlyst 70 catalysts, respectively, and the catalytic activity ratios of r1 / r2 for the hydrolysis of various disaccharides and malto-oligosaccharides. .Whenever blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is broken down via hydrolysis to release glucose monomers that cells can absorb and use. Structural polysaccharides Although . Partial hydrolysis of starch and glycogen produces the disaccharide maltose together with low molecular weight dextrans, polysaccharides in which glucose .Hydrolysis. Google Classroom. About. Transcript. Polysaccharides, such as starch, chitin, glycogen, and cellulose, can be broken down into monosaccharides. This .
Review. Monosaccharide composition analysis of polysaccharides from natural sources: Hydrolysis condition and detection method development. DanLiua, .
This color test is sensitive enough to detect even minute amounts of starch in solution. Figure 16.7.1 16.7. 1: Amylose. (a) Amylose is a linear chain of α-D-glucose units joined together by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. (b) Because of hydrogen bonding, amylose acquires a spiral structure that contains six glucose units per turn. Carbohydrates which on hydrolysis give indefinite or large no. of monosaccharides (more than 10) are called polysaccharides. They contain a large number of monosaccharide units joined together by .
Disaccharides (C 12 H 22 O 11) are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the OH group of a second monosaccharide. The disaccharides differ from one another in .
This page titled 1.18: Glycosides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kirk McMichael. Today we'll look in more detail at the chemistry of that hemiacetal linkage. In particular, we'll recall how hemiacetals are converted to acetals.

5637. As the name implies, polysaccharides are large high-molecular weight molecules constructed by joining monosaccharide units together by glycosidic bonds. They are sometimes called glycans. The most important compounds in this class, cellulose, starch and glycogen are all polymers of glucose. This is easily demonstrated .
hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides 5637. As the name implies, polysaccharides are large high-molecular weight molecules constructed by joining monosaccharide units together by glycosidic bonds. They are sometimes called glycans. The most important compounds in this class, cellulose, starch and glycogen are all polymers of glucose. This is easily demonstrated .
Glycosidases are an important class of enzymes for performing the selective hydrolysis of glycans. Although glycans can be hydrolyzed in principle by acidic water, hydrolysis with high selectivity using nonenzymatic catalysts is an unachieved goal. Molecular imprinting in cross-linked micelles afforded water Most popular 2021 chemical biology articles
This video describes the acid hydrolysis of sucrose and starch.Disaccharides (C 12 H 22 O 11) are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the OH group of a second monosaccharide.
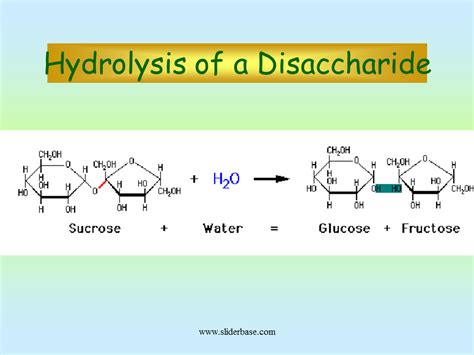
Hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides Disaccharides and polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed (broken down), given sufficient time, into their constituent monosaccharides. In the laboratory hydrolysis can be achieved by reacting the di- and poly- saccharides with acid. Acid hydrolysis of disaccharides will produce the .
Disaccharides and polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or specific enzymes. When a disaccharide is hydrolyzed, the products are the individual monosaccharides. When a polysaccharide is hydrolyzed, the products will depend on how long the mixture is allowed to react, the concentration of acid or enzyme, and other .hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides Polysaccharides are very large polymers composed of tens to thousands of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic linkages. The three most abundant polysaccharides are starch, glycogen, and cellulose. These three are referred to as homopolymers because each yields only one type of monosaccharide (glucose) after .
Disaccharides and oligosaccharides in mild acidic conditions are hydrolyzed into their constituent monosaccharides. The fructofuranosyl linkages of the fructooligosaccharides are quite susceptible to acid hydrolysis. Polysaccharides are also hydrolyzed into their constituent monosaccharides by acid hydrolysis, but the conditions necessary for .
Table 2.3 Synthesis of polysaccharides catalyzed by xylanase, 4-glucanohydrolase, and amylase. Full size table. Polysaccharides composed of glucose residues linked through β- (1 → 3)-glycosidic linkages, i.e., (1 → 3)-β-glucans, such as curdlan, laminarin, and schizophyllan, are found in nature.Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides Disaccharides (C 12 H 22 O 11) are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the OH group of a second monosaccharide. The disaccharides differ from one another in .
The net result of these actions are numerous disaccharides and polysaccharides. Enzymes attached to the enterocycytes of the small intestine break these down to monosaccharides. Hydrolysis by amylase: Both the parotid and pancreatic amylases hydrolyse the 1:4 link, but not the terminal 1:4 links or the 1:6 links. 1. By condensation of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule. 2. By condensation of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule. 3. By evaporation of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule. 4. By hydrolysis of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule. The condensation of two glucose monomers leads to the formation of.You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Question: In the Hydrolysis of Disaccharides and Polysaccharides portion of the lab, starch should give one positive iodine test and one negative iodine test. Explain why. In the Hydrolysis of Disaccharides and Polysaccharides portion of the lab .
The Lottery Sambad 20 Tarik result at 1 PM is impatiently awaited by players who have bought tickets for the morning draw. The 20 tarikh ka lottery sambad fax is also declared on the official Sambad website and can be viewed in local newspapers. Check the 1 PM result below. Players who match the winning number with 20 tarikh ke .
hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides|Hydrolysis of Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides